Waqf Board vs Hindu Endowment Board vs Church Trust
Sanathana board not yet created its managed by state endowment boards. which includes all government officials regardless of religion.

| Aspect | Waqf Board | Hindu Endowment Board | Catholic Church |
|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Islam | Hinduism | Christianity |
| Governing Law | Waqf Act, 1995 | Varies by state – e.g., Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Act, 1951 (Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, etc.) | Indian Trusts Act, 1882 / Societies Act / Canon Law |
| Administered By | Central & State Waqf Boards | State Government Endowment Departments | Independent Church Bodies / Dioceses / Registered Trusts |
| Authority Formation | Statutory body under Ministry of Minority Affairs | Statutory body under State Government | Non-statutory or religious bodies |
| Purpose | Management of Waqf properties for Muslim welfare (charity, education, religion) | Management of Hindu temples and religious endowments | Management of Church properties and religious services |
| Key Responsibilities | Survey, record, protect, and manage waqf assets | Maintain temple records, appoint trustees, manage assets | Administer churches, schools, charities, and lands |
| Revenue Usage | Religious, educational, and charitable purposes | Temple maintenance, festivals, community services | Religious services, schools, healthcare, charity |
| Appointment of Members | Nominated by govt. and elected from Muslim community | Appointed by State Governments | Appointed by religious heads or trust members |
| Jurisdiction | Muslim religious properties only | Hindu temples and endowments under state’s purview | Christian churches and related properties |
| Autonomy | Semi-autonomous but under government oversight | Limited autonomy, high government control | High autonomy depending on trust registration |
does hindu required in endowment department?
yes,
The Hindu Religious Institutions and Charitable Endownments Act, 1997 pdf
does government take money from temples
Yes, governments in some Indian states collect a portion of temple income. This is typically done under the Hindu Religious Institutions and Charitable Endowments Acts, with variations in the specific percentage collected by each state. For instance, in Karnataka, temples with over ₹1 crore annual income contribute 10% to a Common Pool Fund.
TN govt melts 1,000 kg temple gold, earns Rs 17.81 cr annual interest
Temples earning more than Rs 100 crore will be managed by dedicated trust boards, similar to the TTD system, to ensure proper financial management and accountability
source; economic times
-
Purpose of the collection:
The collected funds are often used for the upkeep and maintenance of temples, audit fees, and to support government-run schemes.
-
Variations by state:
The percentage of income taken by the government varies between states, and some states may have exemptions for smaller temples.
-
State-level regulation:
Many states have laws that regulate temple administration, including the use of temple funds.
-
Public good:
Some argue that these funds can be used for the public good, while others argue that temples should have autonomy over their finances.
-
Controversy:The practice of government taking temple funds has faced criticism, with some alleging it is a form of misappropriation.
Telangana Budget proposes Yadagirigutta Temple Board; Endowments department gets ₹190 crore
March 19, 2025 02:41 pm IST – HYDERABAD
source the hindu
Yadadri temple in Telangana sets new all-time high record in one-day income at Rs 1.09 crore
Sunil Mungara / TNN / Nov 13, 2022, 21:19 IST timesof india
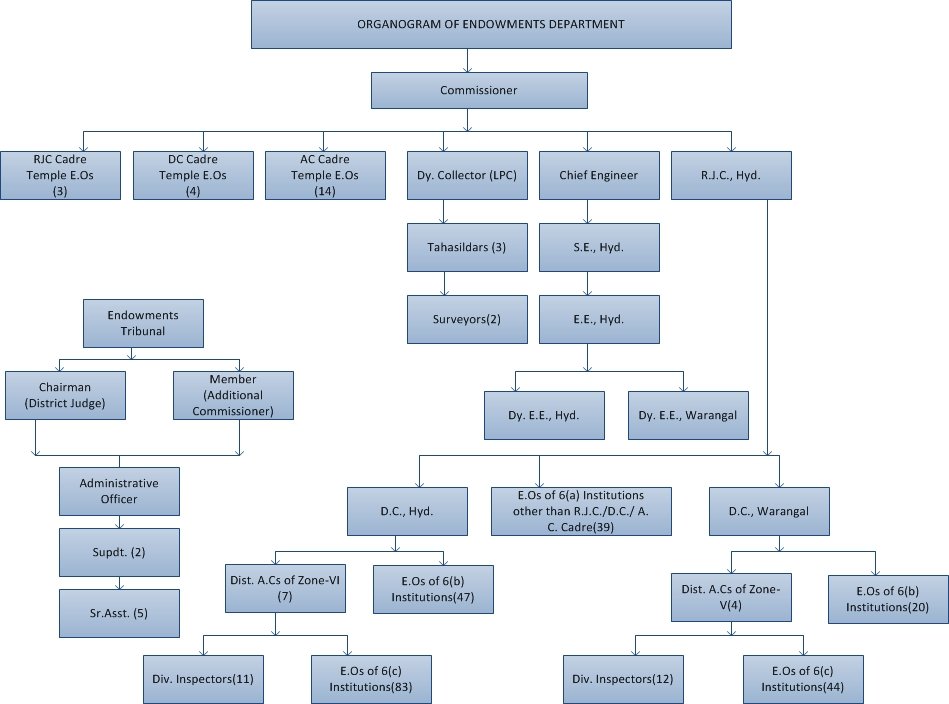
Hindu endoment department structure ex telangana
Commissioner >> regional and divisonal level >>
Who is commissioner of telangana endowment board 2025?
he Commissioner of the Telangana Endowments Department in 2025 is Sri V. Anil Kumar, IAS (Retd.). He also serves as the Commissioner of Civil Supplies Department for the Government of Telangana.
Joint Commissioners at the regional level
list of joint commissioners in telangana endowment board 2025?
He is empowered to appoint
non-hereditary trustees and approve the budgets
for religious institutions assessed under Section
46(i) of the Act.
Assistant Commissioners at the divisional level.
endowment Inspector
Inspector posts have been shifted to the Commissioner’s Office from the Divisional Level.
Verification Officers
Verification Officer in the cadre of Deputy
Commissioner to verify and appraise jewels and
other valuable articles and prepare an appraisal
report for approval.
Conservation Wing
14. The Engineers and Draughting Officers
are incharge
Temple Administration
15. Each Religious Institution and Charitable
Endowment is a separate legal entity and is
administered by its trustees who are empowered
to appoint its employees.
Executive Officers
https://www.telangana.gov.in/departments/endowments/
in the endowment tribunal district judge is the chairman all other goverment officer not related to religion
Hindu endowment act audit process
Audit of Hindu Religious and Charitable Institutions
The Hindu Religious Institutions and Charitable Endownments Act, 1997
Act 33 of 2001
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Religious_and_Charitable_Endowments_Department
hindu religious endowments act history of modification
The initial Religious Endowments Act of 1863 introduced Western legal principles but was later superseded by state-level acts like the Madras Hindu Religious Endowments Act of 1925. Following independence, states enacted their own acts, including the Madras Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Act of 1951 and the Tamil Nadu HR&CE Act of 1959, which faced challenges in court.
-
This act aimed to regulate Hindu religious endowments, introducing Western legal principles for managing temple properties and finances.
-
Madras Hindu Religious Endowments Act of 1925:
This act, passed by the Madras government, established the Hindu Religious Endowments Board (HREB) to oversee temple management.
-
Other State Acts:Similar acts were passed in other states, like the Orissa Hindu Religious Endowments Act of 1939, reflecting a broader trend of government intervention in temple administration during the colonial period.
waqf Board Members waqf act 1955 all muslims
. Central Waqf Council (CWC): Advisory body under the Ministry of Minority Affairs,
guiding Waqf administration. (includes non muslims as under central waqf
(10 members in Muslim category)
(i) Three persons to represent Muslim organisations having all India character and national
importance;
(ii) Chairpersons of three Boards by rotation;
(iii) One person to represent the mutawallis of the waqf having a gross annual income of five
lakh rupees and above;
(iv) Three persons who are eminent scholars in Muslim law; another category (12 members). Out of this category two member will be nonMuslim. Remaining all will be Muslims.
ii. State Waqf Boards (SWBs): Custodians of Waqf properties, responsible for
management, protection, and utilization. (all muslims but 2014 act added 2 non muslims )
iii. Waqf Tribunals: Judicial bodies for resolving Waqf-related disputes all muslims
when to come hindu board all are govt officials.
As per the Waqf Act, 1995, the members of a State Waqf Board must satisfy certain qualifications:
| Category | Eligibility |
|---|---|
| Muslim Members | Must be a practicing Muslim. |
| Professional Members | Should have expertise in fields like law, finance, administration, or waqf management. |
| MPs/MLAs/MLCs | Must be a Muslim Member of Parliament or State Legislature from the respective state
Owasi brother AIMIM party telangana. |
| Islamic Scholars | Recognized scholar in Islamic theology and jurisprudence. |
| Waqf Contributors | Must contribute to waqf institutions financially or through social service. |
📝 Appointment Process of State Waqf Board Members
-
Formation of the Board:
Each state government forms the board under the supervision of the Ministry of Minority Affairs. -
Nomination & Election:
-
Members are nominated or elected from the Muslim community.
-
Elections are held by electoral colleges (e.g., Muslim MPs, MLAs, mutawallis).
-
Scholars and professionals are usually nominated based on their experience.
-
-
Term:
Members serve a term of five years, unless dissolved earlier by the state government. -
Chairperson Appointment:
The Chairperson is elected by the board members from among themselves.
who is telangana waqf board chair person
ex: manipur waqf board
| Sl. No. | Member’s Name | Position holds | Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shri Md. Abdul Nasir | MLA– 30-Lilong A/C | Chairman |
| 2 | Sheikh Noorul Hassan | MLA– 4- Kshetrigao A/C | Member |
| 3 | Ashab Uddin | MLA-40- Jiriban A/C | Member |
| 4 | Shri M.H. Khan | Addll.Chief Secretary, Govt. of Manipur (Nominee) | Member |
| 5 | Muhammad Azad Khan | Mutawali | Member |
| 6 | Alhaj Md. Iqbal Ahmed | Mutawali | Member |
| 7 | Md. Hafiz Quayamuddin | Theology | Member |
| 8 | Md. Asker Ali Makakmayum | Social Worker | Member |
| 9 | Md. Deepak Shah | Social Worker | Member |
| 10 | Md. Rabi Khan | Advocate | Member |
waqf board introcuing non muslims 2024 act
hinus board maintained by govt reglardlress of religion, and churches using trust where gneral law applies. waqf board has seperate powers.
Central waqf council
9. Give details about the composition of the Waqf Board?
The changes introduced to the constitution of the Waqf Board is designed to create two
categories: one exclusively for Muslims (4 members) i.e,
The following members belonging to Muslim community, namely:-
(i) One mutawalli of the waqf having an annual income of one lakh rupees and above;
(ii) One eminent scholar of Islamic theology;
(iii) Two or more elected members from the Municipalities or Panchayat:
Provided that in case there is no Muslim member available from any of the categories in
sub-clause (c) to (i) to (ii), additional members from category sub-clause (iii) may be
nominated:
Provided that two of total members of the Board appointed under in the clause (c), shall be
women.
Another category (7 members), out of this category, 2 members will be non-Muslim,
excluding ex officio, remaining will be Muslims.
(a) A Chairperson;
(i) one Member of Parliament from the State or, as the case may be, the National
Capital Territory of Delhi;
(ii) one Member of the State Legislature;
(b) Two persons who have professional experience in business management, social work,
finance or revenue, agriculture and development activities:
(c) One officer of the State Government, not below the rank of Joint Secretary to the State
Government; ex officio member
(d) One Member of the Bar Council of the concerned State or Union territory:
Provided further that two of the members of the Board appointed under this sub-section,
shall be non-Muslim, excluding ex officio member
Provided also that the Board shall have at least one member each from Shia, Sunni and
other backward classes among Muslim Communities;
Now representation of Muslim women is being ensured. As per section 14(1) in other
category there is no bar for nomination of women members. Only restriction is that there
will be two non-Muslim members.
The composition of State Waqf Boards has further been expanded to include two nonMuslim members, one member from Shia, Sunni, Bohra, Aghakhani, and other backward
classes among Muslims. Which will promote inclusivity and diversity in waqf property
management
Audit of Hindu Religious and Charitable Institutions
19. Under section 87(3) of the Hindu
Religious and Charitable Endowments Act, all
religious institutions whose annual income is not
less than Rs.5 lakh shall be subjected to
concurrent audit and all religious institutions with
income not less than Rs.1,000/- shall be audited
annually and under section 88, audit reports have
to be submitted to the authorities under the Act.
For this purpose, an audit fee from 1.5 percent to
4 percent of the assessable income is collected
under section 92(2).
Appointment of Trustees
Assistant Commissioner is empowered to constitute the Board of Trustees
22. Non-hereditary trustees are appointed for
administering religious institutions under the
Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Act.
Accordingly, the Board of Trustees consists of
three to five members. Of these members, one
shall belong to Scheduled Castes / Scheduled
Tribes and one shall be a Woman. The tenure of
the Board is two years.
Qualifications for appointment of Trustees
23. The following qualifications have been
prescribed under Section 25A for a person to be
appointed as a Trustee: –
a) He must have faith in God;
b) He must possess good conduct and
reputation. Also, he must command
respect in the locality in which the religious
institution or endowment is situated;
c) He must have sufficient time and interest
to attend the affairs of the religious
institution or endowment.
Trustees role in endowment board