top 20 Netstat and SS commands, along with their use cases: netstat deprectated use ss.
| Netstat Command | SS Command | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
netstat -a |
ss -a |
Show all active connections (TCP/UDP) and listening ports. |
netstat -at |
ss -t |
Show all active TCP connections. |
netstat -au |
ss -u |
Show all active UDP connections. |
netstat -l |
ss -l |
Show only listening ports. |
netstat -lt |
ss -lt |
Show only listening TCP ports. |
netstat -lu |
ss -lu |
Show only listening UDP ports. |
netstat -n |
ss -n |
Display numeric IP addresses instead of resolving hostnames. |
netstat -anp |
ss -tanp |
Show all active connections with process ID (PID). |
netstat -i |
ip -s link |
Display network interface statistics (packets sent/received). |
netstat -r |
ip route show |
Display the routing table (similar to route -n). |
netstat -s |
ss -s |
Show network traffic statistics for all protocols. |
netstat -c |
watch ss -s |
Continuously update and display network statistics. |
netstat -tp |
ss -tp |
Show TCP connections with associated process names. |
netstat -g |
ip maddr show |
Display multicast group memberships. |
netstat -M |
ss -M |
Show NAT masqueraded connections. |
netstat --tcp |
ss --tcp |
Show only TCP socket connections. |
netstat --udp |
ss --udp |
Show only UDP socket connections. |
netstat -o |
ss -o state established |
Show TCP connection timers. |
netstat -p |
ss -p |
Display programs (PIDs) associated with connections. |
netstat -g |
ss -g |
Display group memberships for sockets. |
Netstat Commands (Deprecated in Favor of SS)
Netstat (Network Statistics) is a command-line tool for monitoring network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
netstat -a |
Show all active connections and listening ports. |
netstat -at |
Show all active TCP connections. |
netstat -au |
Show all active UDP connections. |
netstat -l |
Show only listening ports. |
netstat -lt |
Show only listening TCP ports. |
netstat -lu |
Show only listening UDP ports. |
netstat -n |
Display addresses and ports in numeric format. |
netstat -anp |
Show all active connections with PID and process name. |
netstat -i |
Show network interface statistics. |
netstat -r |
Display the routing table. |
netstat -s |
Show network statistics for all protocols. |
netstat -c |
Continuously print network statistics. |
⚡ SS (Socket Statistics) – A Faster Alternative to Netstat
ss is a modern replacement for netstat, providing faster and more detailed socket statistics.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ss -tuln |
Show all listening TCP & UDP ports in numeric format. |
ss -tan |
Show all active TCP connections. |
ss -uan |
Show all active UDP connections. |
ss -s |
Display a summary of all network connections. |
ss -tp |
Show TCP connections with process names. |
ss -n state established |
Show only established connections. |
ss -o state established |
Show established connections with timer details. |
ss -lt |
Show listening TCP ports. |
ss -lu |
Show listening UDP ports. |
ss -lx |
Show listening UNIX sockets. |
Netstat & SS Commands with Examples Cheat Sheet
This guide covers the top Netstat and SS (Socket Statistics) commands with practical examples. Netstat is now largely replaced by SS due to its speed and efficiency.
🌐 Netstat Commands (Deprecated but Still Useful)
Netstat (Network Statistics) is used to display network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships.
1️⃣ Show All Active Connections
📌 Example Output:
Lists all active connections and listening ports.
2️⃣ Show Active TCP Connections
📌 Example Output:
Displays all TCP connections.
3️⃣ Show Active UDP Connections
📌 Example Output:
Displays all UDP connections.
4️⃣ Show Only Listening Ports
📌 Example Output:
Shows ports that are actively listening for incoming connections.
5️⃣ Show Only Listening TCP Ports
📌 Example Output:
Lists only TCP ports that are in the listening state.
6️⃣ Show Only Listening UDP Ports
📌 Example Output:
Lists only UDP ports that are in the listening state.
7️⃣ Show Numeric Addresses Instead of DNS Names
📌 Example Output:
Displays IP addresses and port numbers without resolving domain names.
8️⃣ Show Active Connections with Process ID (PID)
📌 Example Output:
Lists all active connections with process ID and process name.
9️⃣ Show Network Interface Statistics
📌 Example Output:
Displays network interface statistics such as sent/received packets.
🔟 Display the Routing Table
📌 Example Output:
Shows the kernel routing table (same as route -n).
1️⃣1️⃣ Show Network Statistics for All Protocols
📌 Example Output:
Summarizes network traffic and errors for all protocols.
1️⃣2️⃣ Continuously Print Network Statistics
📌 Example Output:
Keeps updating network statistics in real-time.
⚡ SS (Socket Statistics) – Faster Alternative to Netstat
The ss command is a modern replacement for netstat, offering faster performance and more details.
1️⃣3️⃣ Show All Listening TCP & UDP Ports
📌 Example Output:
Lists all listening TCP and UDP ports.
1️⃣4️⃣ Show All Active TCP Connections
📌 Example Output:
Displays active TCP connections without resolving hostnames.
1️⃣5️⃣ Show All Active UDP Connections
📌 Example Output:
Displays active UDP connections.
1️⃣6️⃣ Show Summary of All Network Connections
📌 Example Output:
Provides a summary of all active connections.
1️⃣7️⃣ Show TCP Connections with Process Names
📌 Example Output:
Lists TCP connections along with process names and PIDs.
1️⃣8️⃣ Show Only Established Connections
📌 Example Output:
Displays only established connections.
1️⃣9️⃣ Show Established Connections with Timer Details
📌 Example Output:
Shows TCP timer details for established connections.
2️⃣0️⃣ Show Listening UNIX Sockets
📌 Example Output:
Lists listening UNIX domain sockets.
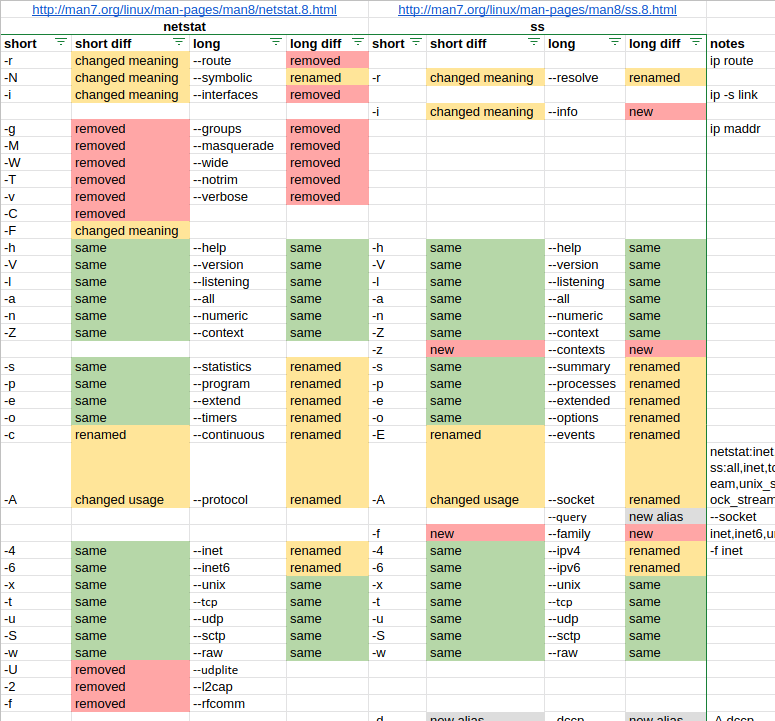
ss command Common options
| Long option | Short option | Related action |
|---|---|---|
| –all | -a | Show both listening and non-listening sockets |
| –events | -E | Show sockets that are destroyed (closed connections) |
| –info | -i | Internal TCP information |
| –ipv4 | -4 | Only IPv4 sockets displayed |
| –ipv6 | -6 | Only IPv6 sockets displayed |
| –listening | -l | Only show listening sockets |
| –no-header | -H | Do not show the header, great for one-liners and parsing the output |
| –numeric | -n | Numeric output, conversion of names (services, ports) is skipped |
| –processes | -p | Show related process that interacts with the socket |
| –resolve | -r | Try resolving numeric values for addresses and ports |
| –summary | -s | Display a summary with statistics at the top |
| –tcp | -t | Show TCP sockets |
| –udp | -u | Show UDP sockets |
Netstat & SS Command – Interview Questions and Answers
Here are some commonly asked interview questions on Netstat and SS (Socket Statistics), along with their detailed answers.
1️⃣ What is the purpose of the netstat command?
✅ Answer:netstat (Network Statistics) is a command-line tool used to display network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, and listening ports. It helps in diagnosing network-related issues and monitoring traffic.
Example:
🔹 Use case: Show all active network connections with numeric IP addresses and ports.
2️⃣ Why is ss preferred over netstat?
✅ Answer:
The ss (Socket Statistics) command is a modern replacement for netstat. It provides faster and more detailed information about socket connections because it directly reads from kernel space instead of /proc.
Example Comparison:
🔹 ss is faster and shows more detailed socket information.
3️⃣ How do you list all listening TCP and UDP ports?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Explanation:
-
-t→ TCP -
-u→ UDP -
-l→ Listening -
-n→ Numeric format (no DNS resolution)
4️⃣ How do you check which process (PID) is using a specific port?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps identify which process is occupying a network port.
5️⃣ How do you view all active TCP connections?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps in monitoring active network sessions.
6️⃣ How do you find all UDP connections?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Useful for troubleshooting DNS and VoIP traffic.
7️⃣ How do you check the routing table using Netstat?
✅ Answer:
🔹 Alternative:
🔹 Use case: Shows the system’s network routing table.
8️⃣ How do you display network statistics for all protocols?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Useful for monitoring packet transmission statistics.
9️⃣ How do you continuously monitor network connections?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Keeps an updated view of the network traffic.
🔟 What command shows connections in an “ESTABLISHED” state?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps identify active and ongoing connections.
1️⃣1️⃣ How do you check which user owns a network connection?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Useful for security audits and debugging.
1️⃣2️⃣ How do you find which ports are commonly used?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps detect frequently accessed ports.
1️⃣3️⃣ How do you find if a specific port (e.g., 443) is in use?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps check whether a service is running on a specific port.
1️⃣4️⃣ How do you list UNIX domain socket connections?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps debug UNIX interprocess communication (IPC).
1️⃣5️⃣ How do you identify orphaned sockets?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Useful for detecting idle or abandoned connections.
1️⃣6️⃣ How do you check firewall-related network activity?
✅ Answer:
🔹 Use case: Lists multicast group memberships.
1️⃣7️⃣ What is the difference between netstat -g and ss -g?
✅ Answer:
Both commands display multicast group memberships, but ss -g provides more detailed and faster output.
1️⃣8️⃣ How do you check if a specific remote IP is connected?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Helps identify remote machine connections.
1️⃣9️⃣ How do you save the output of Netstat/SS for analysis?
✅ Answer:
🔹 Use case: Helps store network activity logs.
2️⃣0️⃣ How do you monitor real-time connections?
✅ Answer:
Using netstat:
Using ss:
🔹 Use case: Provides real-time network monitoring.
Netstat manual https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/netstat.8.html
ss manual https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/ss.8.html